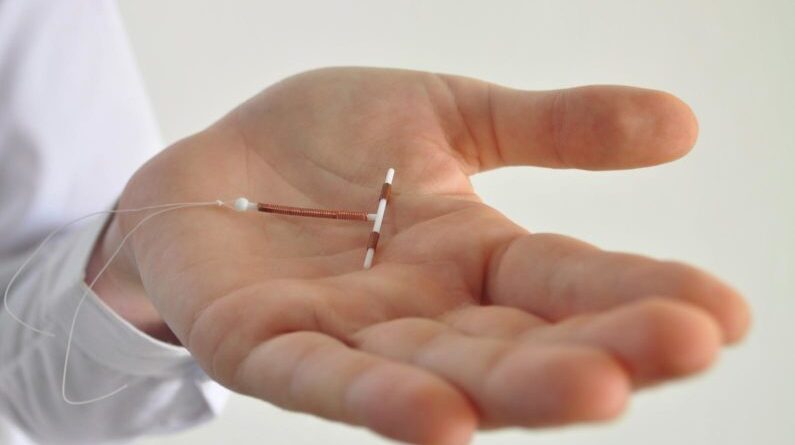
A recent study published in The British Medical Journal found that low-dose estrogen plus levonorgestrel birth control pills seem to be the safest in terms of cardiovascular risk. It is important to note that all hormonal birth control pills have the potential to cause vulvodynia. The tissue in the vulvar vestibule has androgen receptors so …
Continue Reading